World Cardiology 2019
About Conference
Theme: A Step towards Healthy Heart
Cardiology 2019 is hosted by EuroSciCon and it is focuses on the major issues of heart diseases and cardiological injury that is common in people. This is of great concern as the survival of future generation is at stake. Heart-healthy life style is essential for overall health so we invite Researchers, Cardiologists, Doctors, Physicians, Academicians, Industrialists and Dieticians to give the world a better solution to this problem. The conference will be a platform to globalize one research, to share scientific experiences, to gain knowledge on new diagnostics methods and treatment procedures. The conference is scheduled on February 25-26, 2019 in Paris, France. We invite sponsors and exhibitor to showcase your products to our participants and make it reach the public through them. We request you to make use of this opportunity to make the world a better place to live in.
What’s New?
Cardiology 2019 includes international attendee workshops, lectures and symposia, including a designated registration area, a refreshment break and gala lunch. Cardiologist and Researchers can join the EuroSciCon as an international member to receive discounts on registration. So come and join leading experts and medical professionals from February 25-26, 2019 in Paris, France to keep up with the rapidly accelerating pace of change that is already having an impact on the field of Heart disease and Interventional cardiology.
About Paris
Paris, France's capital is a significant European city and an overall group for craftsmanship, style, gastronomy and society. Its nineteenth century cityscape is scattered by wide paths and the River Seine. The city is known for its bistro culture and architect boutiques along the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré. Paris is the city of adoration, motivation, workmanship and mold. It has a populace of more than 2million individuals and is isolated into 20 local. Paris has a considerable measure of fascinating design and historical centers to offer; among them the well-known traveller place to visit is the Eiffel Tower. A critical number of the acclaimed streets and city building territories structures where changed by Haussmann and Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoleon Bonaparte). The paths where made substantially more extensive, places and squares where manufactured and the structures completely altered. Paris has an epithet called "La Ville-Lumiere. The well-known spots to visit in Paris are Notre Dame Cathedral which is Roman Catholic Cathedral arranged in the eastern portion of the city, Louver Museum which is situated at the core of Paris , Champs Elysees which is an Arc of Triumph, Montmartre which is a slope situated at the north of Paris and its stature is 130 meter, it is best known White Domed Basilica of the holy heart at the best, Quartier Latin which is known as the popular private garden situated on the left bank of the seine around the Sorbonne, Disneyland Paris which is found 32 km from focal Paris , it has two amusement parks – Disneyland and Walt Disney studios.
Sessions and Tracks
Track 1: Clinical Cardiology
Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with diseases and abnormalities of the heart . The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a speciality of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called as cardiac surgeons, a speciality of general surgery.
Track 2: Invasive cardiology
Invasive cardiology uses open or minimally-invasive surgery to identify or treat structural or electrical abnormalities within the heart structure. When plaque clogs your arteries, it becomes difficult for blood to flow normally. Angioplasty inserts a tiny balloon into your clogged vein and pushes plaque against the walls, allowing for increased blood flow. Stenting is usually done in conjunction with angioplasty. A cardiac stent is a small metal coil which permanently holds a clogged vein open.
- Angioplasty
- Stenting
Track 3: Non-invasive cardiology

Non-invasive cardiology identifies heart problems without using any needles, fluids, or other instruments which are inserted into the body. Nuclear cardiology is a non-invasive study of cardiovascular disorders by means of various types of imaging which may use radioactive elements. Echocardiograph is the usage of ultrasound waves to create images of the heart and surrounding structures in order to identify how well the heart pumps blood, infections, and structural abnormalities. Cardiac electrophysiology is the study and testing of the electrical currents which generate heartbeats. Stress tests usually involve exercise which is monitored by our cardiologist. These exercises provide our cardiologist information about how our heart performs under physical stress. Heart monitors may also be called a Holter monitor or cardiac event recorder. Heart monitors are essentially tape recorders for our heart electrical activity over a set amount of time. CT scans produce images which our cardiologist can examine for heart disease and atherosclerosis.
- Echocardiography
- Cardiac electrophysiology
- Stress tests
- Heart monitors
- CT scans
Track 4: Interventional Cardiology
Interventional cardiology is a non-surgical option which uses a catheter – a small, flexible tube – to repair damaged or weakened vessels, narrowed arteries, or other affected parts of the heart structure. Heart valve disease occurs when the valves which control blood flow into the heart chambers are not working correctly. In Peripheral vascular disease heart can also be affected by clogged or hardened veins and arteries which are in other parts of our body. Angioplasty is is an intervention to dilate either arteries or veins. Coronary angioplasty/Percutaneous coronary intervention is an intervention for the treatment of coronary artery disease. It can be culprit-vessel revascularization only or complete revascularization.Valvuloplasty it is the dilation of narrowed cardiac valves (usually mitral, aortic, or pulmonary). Percutaneous approaches can be employed to correct atrial septal and ventricular septal defects, closure of a patient ductus arteriosus, and angioplasty of the great vessels. Percutaneous valve replacement is an alternative to open heart surgery, percutaneous valve replacement is the replacement of a heart valve using percutaneous methods. This is performed on the aortic valve, pulmonary valve and recently the mitral valve.Percutaneous valve repair is performed on the mitral valve using the MONARC system or MitraClip system. Coronary thrombectomy involves the removal of a thrombus (blood clot) from the coronary arteries.
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart valve disease
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Angioplasty
- Coronary angioplasty/Percutaneous coronary intervention
- Congenital heart defect correction
- Percutaneous valve replacement
- Percutaneous valve repair
- Coronary thrombectomy
Track 5: Pediatric Cardiology
Pediatric Cardiologists care for patients with congenital or acquired cardiac and cardiovascular abnormalities. The scope of pediatric cardiology practice is extensive. Pediatric Cardiologists evaluate and care for fetuses, neonates, infants, children, adolescents, young adults, and adults.
Special areas of clinical and academic interest include: Intensive Cardiac Care, Cardiac Catheterization and Intervention, Electrophysiology, Imaging, Fetal Cardiology, Exercise Physiology, Preventive Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation, and Pulmonary Hypertension.
cardiovascular diseases seen in paediatrics are as follows :
- Aortic senosis
- Arrhythmias
- Atrial sptic defect
- Cardiac failure
- Cardiomyopathy
- Coarctation of aorta
- Congenital heart disease
- Endocardial cushion defect
- Kawasaki disease
- Pulmonary atresia and pulmonary stenosis
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection
- Transposition of great arteries
- Tricus arteriosus
- Ventricular septal defect
Track 6: Cardiac Imaging
A physician may recommend cardiac imaging to support a diagnosis of a heart condition. Medical speciality professional organizations discourage the use of routine cardiac imaging during pre-operative assessment for patients about to undergo low or mid-risk non-cardiac surgery because the procedure carries risks and is unlikely to result in the change of a patient management. Stress cardiac imaging is discouraged in the evaluation of patients without cardiac symptoms or in routine follow-ups.
- Magnetic resonance
- Coronary CT calcium scan
- Computed tomography angiography
- Positron emission tomography
- Echocardiogram
- Intravascular ultrasound
- Fractional flow reserve
- Coronary catheterization
Track 7: Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. Cardiovascular disease includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Hypertensive heart disease
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart arrhythmia
- Congenital heart disease
- Valvular heart disease
- Carditis
- Aortic aneurysms
- Peripheral artery disease
- Thromboembolic disease
- Venous thrombosis.
Track 8: Heart Failure
Heart failure can be brought on by many conditions that damage the heart including: Coronary artery disease, this is a disease of the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to your heart. It decreases blood flow to our heart muscles. If the arteries narrow or get blocked our heart becomes starved for oxygen and nutrients and can't pump as well. Heart attack this may happen when a coronary artery is blocked suddenly, which stops the flow of blood to our heart muscles. Cardiomyopathy this is damage to our heart muscles that can be caused by artery or blood flow problems, infections, alcohol, drug abuse and other diseases or genetic issues can also bring it on. Make sure your doctor knows your family's health history. Conditions that overwork the heart. These include things like high blood pressure, heart valve disease, thyroid disease, kidney disease, diabetes, or heart defects you've had since you were born.
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Conditions that overwork the heart.
- Cardiomyopathy
Stages of Heart Failure:
Stage A. This is the period when you are at risk for heart failure. You may be in this stage if you have:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
- Metabolic syndrome
You may also be at risk if you have a history of:
- Cardiotoxic drug therapy
- Alcohol abuse
- Rheumatic fever
- Family members with cardiomyopathy
Stage B. You're in this phase if you never had symptoms of heart failure but you're diagnosed with systolic left ventricular dysfunction, which means the left chamber of your heart doesn't pump well. You may be in this group if you had or have:
- Heart attack
- Valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
Stage C. You're in this phase if you have systolic heart failure along with symptoms such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Less ability to exercise
Stage D. You're in this phase if you have systolic heart failure and advanced symptoms after you get medical care.
Track 9: Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease

Even when glucose levels are under control it greatly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. That's because people with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, may have the following conditions that contribute to their risk for developing cardiovascular disease.
- Glycemic control
- Obesity
- Dyslipidemia
- Hypertension
- Oxidative stress
- Epigenetics
- Inflammatory cascade, atherosclerosis
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy
Track 10: Women And Cardiac Arrhythmia

Several prominent electrophysiologic differences have been noted between the sexes. By 5 years of age, girls have a higher heart rate than do boys, which might be explained by a shorter sinus node refractory time. The shorter QT interval in men is noted during puberty, as sex hormone levels rise. The length of the QT interval in men increases linearly through adulthood until the age of 50, when it becomes similar to that of women, which correlates with the decrease in androgen levels. Furthermore, QRS amplitude and duration are greater in men, consequent to a higher cardiac mass and thicker left ventricular walls.
- Effects of Sex Hormones
- Atrial Fibrillation
Track 11: Critical Cardiac Care
Critical cardiac care (CIC) which is also known as coronary care unit (CCU) is a hospital ward specialized in the care of patients with heart attacks, unstable angina, cardiac dysrhythmia and various other cardiac conditions that require continuous monitoring and treatment or first aid treatment till the doctor comes. There are also units available in the hospitals to take care of the emergency situation. The Cardiac intensive care unit (CICU) is a specialized ICU dealing with cardiac patients and is usually staffed by cardiologists. It offers critical care staff especially trained in acute coronary syndromes and has additional technology such as intra-aortic balloon pumps etc.
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Clot busting medicine
- Oxygen therapy
- Emergency medicine
- Acute coronary care
- Subacute coronary care
Track 12: Cardiac Surgery
The surgery done to heart by an professional cardiologist to treat its dysfunction. There are many different types of cardiac surgeries available to cure different type of cardiac problems some of them are mentioned below
- Open heart surgery
- Modern beating heart surgery
- Heart transplant
- Coronary artery bypass grafting
- Minimally invasive surgery
Track 13: Cardio-Oncology
Cardio-oncology is the intersection of heart conditions in patients who have been treated for cancer. It is a growing field that aims to optimize the cardiovascular care received by cancer patients before, during and after chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
Track 14: Atherosclerosis
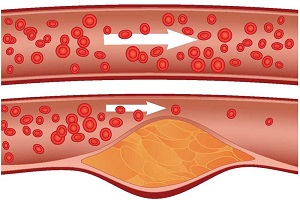
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which the inside of an artery narrows due to the build up of plaque. Initially, there are generally no symptoms. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems depending on the arteries which are affected. Symptoms, if they occur generally do not begin until middle age.
Modifiable:
- Diabetes
- Dyslipidaemia
- Tobacco smoking
- Trans fat
- Abdominal obesity
- Western pattern diet
- Insulin resistance
- Hypertension
Non modifiable:
- Advanced age
- Family history
- Genetic abnormalities
The type of artery affected and where the plaque develops varies with each person. Plaque may partially or totally block blood flow through a large or medium-sized artery in the heart, brain, pelvis, legs, arms or kidneys. When this happens, various diseases may result. These include:
- Coronary heart disease
- Angina
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease
- Chronic kidney disease.
Track15: Obesity and Heart
Obesity has numerous consequences on the cardiovascular system. Chronic accumulation of excess body fat leads to a variety of metabolic changes, increasing the prevalence of CVD risk factors but also affecting systems modulating inflammation. Obesity promotes alterations in other intermediate risk factors such as dyslipidemia, HTN, glucose intolerance, inflammatory state, obstructive sleep apnea/hypoventilation, and a prothrombotic state, as well as probably many additional unknown mechanisms. Obesity also induces a variety of structural adaptations/alterations in CV structure/function. Being obese can raise blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels, lower "good" HDL cholesterol. HDL cholesterol is linked with lower heart disease and stroke risk, so low LDL tends to raise the risk , increase blood pressure and diabetes. In some people, diabetes makes other risk factors much worse. The danger of heart attack is especially high for these people.
Correlation of obesity and heart:
- Obesity and hypertension
- Obesity and coronary heart disease
- Obesity and heart failure
- Obesity and atrial fibrillation
- Obesity and stoke
- Obesity and ventricular arrhythmias
- Obesity and sleep apnea
- Obesity and venous disease
Track 16: Cardiac Medications
These are different class of drugs which are used to treat cardiac diseases and even to prevent occurrence of cardiac failure
- ACE inhibitors: These medications block stress hormones and relieve stress on the heart pumping action. They improve symptoms and reduce hospitalizations for patients with heart failure.
- Antiarrhythmics: These control irregular heartbeats — and maintain a normal heart rate and rhythm.
- Anticoagulants and platelet inhibitors: These cause your blood to take longer to clot, which can reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks that can occur when blood clots get stuck in small blood vessels.
- Antihypertensives: These are commonly used to treat high blood pressure by relaxing and widening blood vessels.
- Beta blockers: These medications are often prescribed to treat angina, high blood pressure, and irregular heart rhythms. They bslock stress hormones and relieve stress on the heart’s pumping action . Relax the blood vessels so blood can move more easily. Improve the heart’s function . Reduce symptoms and lessen the chance of future hospitalizations
- Calcium channel blockers: These are commonly used to treat high blood pressure, coronary artery spasms, and angina. They restrict the normal flow of calcium into the cells of the heart and blood vessels, which discourages smaller vessels from narrowing and going into spasm, and also reduces the heart’s workload and need for oxygen.
- Digitalis glycosides: These strengthen the heart muscle, treat irregular heart rhythms, and improve exercise tolerance.
- Diuretics: These helps in getting rid of our body excess fluid and salt. They are often prescribed for high blood pressure and congestive heart failure.
- Lipid medications: The medications in this category work in different ways depending on which one you’re taking, lipid medications can lower your levels of cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides — as well as treat abnormally low levels of HDL cholesterol.
- Nitrates and other antianginals : These are commonly used to prevent, reduce, or relieve angina pain. They work by relaxing blood vessels and increasing the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart — while reducing the blood pressure that your heart has to pump against.
Track 17: Non pharmacotherapy for cardiovascular diseases
There are some non pharmacotherapies are available to prevent and to control heart diseases. These non pharmacotherapies can be implemented along with pharmacotherapy.
Track 18: Cardiac Care Nursing

Cardiac nursing is a nursing specialty that works with patients who suffer from various conditions of the cardiovascular system. Cardiac nurses help treat conditions such as unstable angina, cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction and cardiac dysrhythmia under the direction of a cardiologist.
Cardiac nurses perform postoperative care on a surgical unit, stress test evaluations, cardiac monitoring, vascular monitoring, and health assessments. Cardiac nurses must have Basic Life Support and Advanced Cardiac Life Support certification. In addition, cardiac nurses must possess specialized skills including electrocardiogram monitoring, defibrillation, and medication administration by continuous intravenous drip.
Cardiac nurses work in many different environments, including coronary care units (CCU), cardiac catheterization, intensive care units (ICU), operating theatres, cardiac rehabilitation centers, clinical research, cardiac surgery wards, cardiovascular intensive care units (CVICU), and cardiac medical wards.
Track 19: Current Research In Cardiology

Cardiology conferences comprises the current research in cardiology contains the new innovative methods that are coming in cardiology related field.
- Statin therapy
- Thrombolytic therapy
- Cardiac rehabilitation
- 3-D imaging
- Wearable technologies
- Wireless technologies and biosensors
- Percutaneous mitral valve repair devices
- 3-D bioprinting
Track 20: Cardiovascular Diseases during Pregnancy

Pregnancy increases the risk of new-onset SVT. This risk is higher in pregnant patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. In the absence of structural heart disease, AF and atrial flutter are rare during pregnancy. Nonsustained ventricular arrhythmias occur in up to 50% of pregnant women, but the clinical risk of sustained ventricular arrhythmia in the absence of structural heart disease is low.
Most antiarrhythmic drugs are classified as category C drugs during pregnancy by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) .Therefore, drug therapy should be used only in patients who have life-threatening arrhythmias or debilitating symptoms. Most β-blockers are classified as category C drugs by the FDA; however, atenolol is classified as a category D drug because it has been implicated in intrauterine growth retardation, and sotalol, pindolol, and acebutolol are classified as category B drugs. Other class C drugs include adenosine, digoxin, and heparin, whereas lidocaine and enoxaparin are class B drugs. Enoxaparin is safe for the fetus, but some formulations contain the preservative benzylalcohol, which can be harmful. Amiodarone is considered a category D drug, and warfarin (category X) should not be used at all during pregnancy because of its teratogenicity.
Track 21: Congenital Heart Therapies
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.
The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditions are associated with heart defects including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Marfan syndrome. Congenital heart defects are divided into two main groups: cyanotic heart defects and non-cyanotic heart defects, depending on whether the child has the potential to turn bluish in color. The problems may involve the interior walls of the heart, the heart valves, or the large blood vessels that lead to and from the heart.
- Hypoplasia
- Obstruction defects
- Septal defects
- Cyanotic defects





















